==定义==
SpringBoot是一个javaweb的开发框架,和SpringMVC类似,对比其他javaweb框架的好处,官方说是简化开发,约定大于配置,you can "just run",能迅速的开发web应用,几行代码开发一个http接口
==主要优点==
为所有Spring开发者更快的入门
开箱即用 ,提供各种默认配置来简化项目配置内嵌式容器简化Web项目
没有冗余代码生成和XML配置的要求
SpringBoot01HelloWorldApplication.java核心配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
//标记这是一个springBoot的应用
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBoot01HelloWorldApplication {
//启动应用
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
//SpringApplication类主要做了如下4件事
//1、推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是Web项目
//2、查找并加载所有可用初始化器,设置到initializers属性中
//3、找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners属性中
//4、推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类,它会在com.mhqdz(Group)目录下找main方法作为主类
SpringApplication . run ( SpringBoot01HelloWorldApplication . class , args );
}
}
@SpringBootApplication注解展开
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
@Target ({ ElementType . TYPE })
@Retention ( RetentionPolicy . RUNTIME )
@Documented
@Inherited
//springBoot的配置
@SpringBootConfiguration
//自动配置
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@AutoConfigurationPackage //自动配置包
@Import ({ AutoConfigurationImportSelector . class }) //自动配置导入选择
//读取spring.factories文件来获取配置
Enumeration urls = classLoader . getResources ( "META-INF/spring.factories" );
//我的文件的实际路径
C: \ Users \ user \ . m2 \ repository \ org \ springframework \ boot \ spring - boot - autoconfigure \ 2.6.1 \ spring - boot - autoconfigure - 2.6.1 . jar ! \ META - INF \ spring . factories
//扫描包
@ComponentScan (
excludeFilters = { @Filter (
type = FilterType . CUSTOM ,
classes = { TypeExcludeFilter . class }
), @Filter (
type = FilterType . CUSTOM ,
classes = { AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter . class }
)}
)
spring.factories文件中的HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration类浅析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet ;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass ;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean ;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty ;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication ;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnWebApplication.Type ;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ServerProperties ;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties ;
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerFactoryCustomizer ;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.filter.OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter ;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory ;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.Encoding ;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean ;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration ;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered ;
import org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter ;
//Configuration表示可以配置的类
@Configuration (
//proxyBeanMethods代理bean的方法
proxyBeanMethods = false
)
//自动配置的配置属性,给出前缀指定配置哪个类,在ServerProperties.class里@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server",ignoreUnknownFields = true),即前缀为server
@EnableConfigurationProperties ({ ServerProperties . class })
//ConditionalOn......: Spring的底层注解 根据不同的条件来判断当前配置或者类是否生效
//详细的分析:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/78251301
@ConditionalOnWebApplication ( type = Type . SERVLET ) //只有运行在web应用里才会加载这个bean,@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication与之相反 不在web应用里才会加载
@ConditionalOnClass ({ CharacterEncodingFilter . class }) //判断某个类是否存在于classpath中,这里判断是否存在编码过滤器
@ConditionalOnProperty ( prefix = "server.servlet.encoding" , value = { "enabled" }, matchIfMissing = true ) //application文件中enabled为true才会加载这个Bean,如果没有匹配上也会加载,因为matchIfMissing=true,默认值是false,prefix是前坠即在application中的配置为server.servlet.encoding.enabled
public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration {
private final Encoding properties ;
//构造函数ServerProperties就是上面@EnableConfigurationProperties({ServerProperties.class})
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration ( ServerProperties properties ) {
this . properties = properties . getServlet (). getEncoding ();
}
@Bean
//需要Bean不存在于应用上下文时才会加载,@ConditionalOnBean与之相反
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public CharacterEncodingFilter characterEncodingFilter () {
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new OrderedCharacterEncodingFilter ();
filter . setEncoding ( this . properties . getCharset (). name ());
filter . setForceRequestEncoding ( this . properties . shouldForce ( org . springframework . boot . web . servlet . server . Encoding . Type . REQUEST ));
filter . setForceResponseEncoding ( this . properties . shouldForce ( org . springframework . boot . web . servlet . server . Encoding . Type . RESPONSE ));
return filter ;
}
@Bean
public HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration . LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer localeCharsetMappingsCustomizer () {
return new HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration . LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer ( this . properties );
}
static class LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer < ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory >, Ordered {
private final Encoding properties ;
LocaleCharsetMappingsCustomizer ( Encoding properties ) {
this . properties = properties ;
}
public void customize ( ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory factory ) {
if ( this . properties . getMapping () != null ) {
factory . setLocaleCharsetMappings ( this . properties . getMapping ());
}
}
public int getOrder () {
return 0 ;
}
}
}
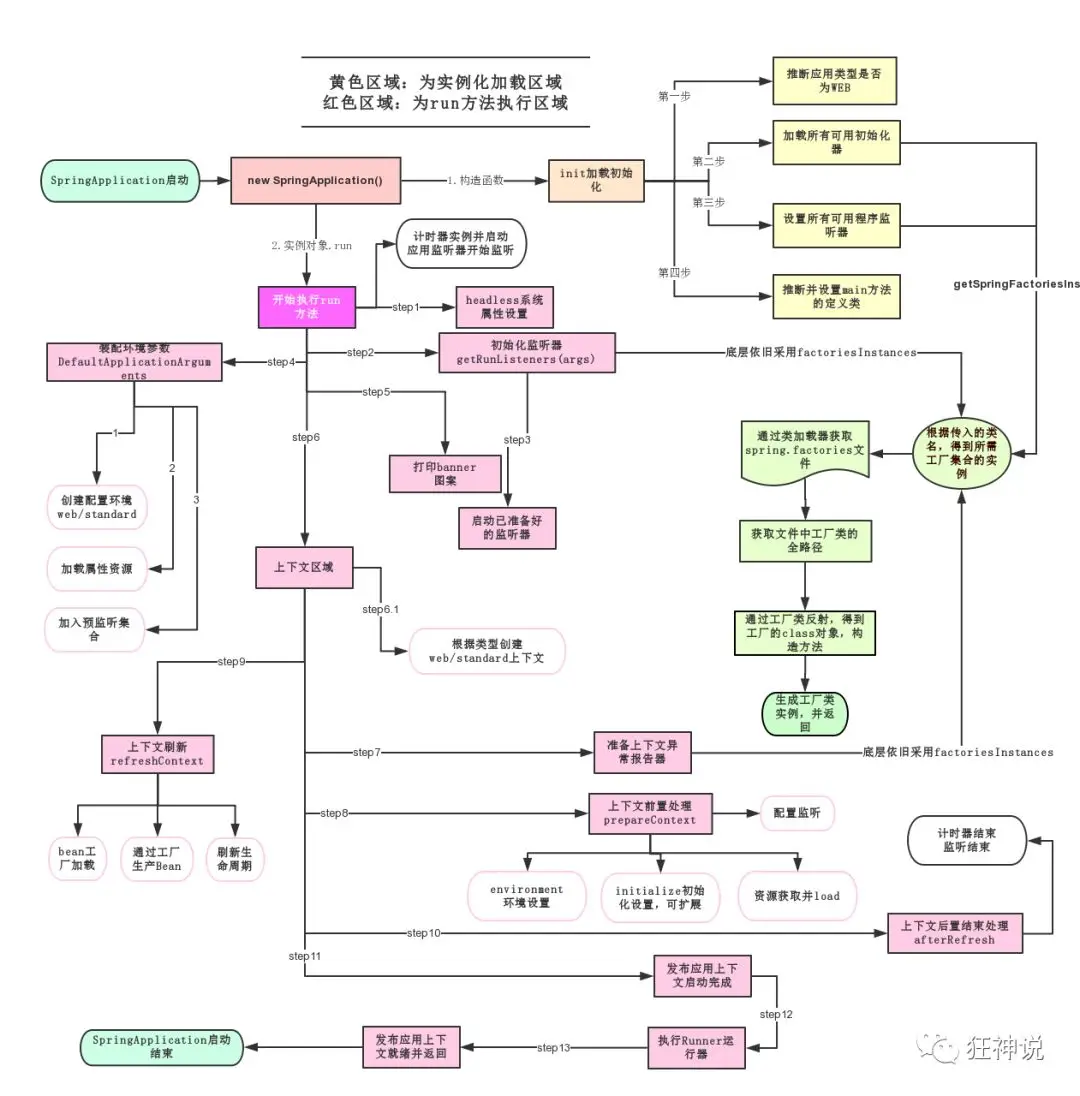
执行流程图
==总结==
1、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2、我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中;
3、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
4、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可;
**xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;**给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性;
pom.xml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
<!-- 父依赖 -->
<parent>
<groupId> org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId> spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version> 2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<!-- web场景启动器:tomcat,dispatcherServlet.xml...使用tomcat作为默认嵌入式容器 -->
<dependency>
<groupId> org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId> spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- springboot单元测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId> org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId> spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope> test</scope>
<!-- 剔除依赖 -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId> org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId> junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- 打包插件,在maven那里package打包,打包前建议先clean一下 -->
<plugin>
<groupId> org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId> spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件 , 配置文件名称是固定的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
//org.springframework.boot对于它的检索
<includes>
<include> **/application*.yml</include>
<include> **/application*.yaml</include>
<include> **/application*.properties</include>
</includes>
application.properties或者application.yml或者application.yaml
其中.yml与.yaml等价.yml是为了对齐.xml
==配置文件可以存在的位置==
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
.\resources\application.yaml
.\config\application.yaml
.\application.yaml
.\resources\config\application.yaml
优先级:
1.项目路径下的config文件夹配置文件 .\config\application.yaml
2.项目路径下配置文件优先级 .\application.yaml
3.资源路径下的config文件夹配置文件优先级 .\resources\config\application.yaml
4.资源路径下配置文件 .\resources\application.yaml
拓展:
可以通过spring.config.location来改变默认的配置文件位置,如
1
java -jar spring-boot-config.jar --spring.config.location= F:/application.properties
YAML是 “YAML Ain’t a Markup Language” (YAML不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写 在开发的这种语言时YAML的意思其实是"Yet Another Markup Language"(仍是一种标记语言)
yaml语法要求严格
1、空格不能省略
2、以缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左边对齐的一列数据都是同一个层级的。
3、属性和值的大小写都是十分敏感的。
有一些简单的函数:如 ${random.uuid}:生成一个uuid,
${person.nmd:我爱你}:如果person.nmd存在则它等于person.nmd否则它就等于 我爱你,用这种方式作为占位符就很灵活
key: value [数字,布尔值,字符串]
字面量直接写在': '后面就可以,字符串默认不用加上双引号或者单引号,类似于go里的:=
注意:
“ ” 双引号,不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符 , 特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思;
比如 :name: “kuang \n shen” 输出 :kuang 换行 shen
’’ 单引号,会转义特殊字符 , 特殊字符最终会变成和普通字符一样输出
比如 :name: ‘kuang \n shen’ 输出 :kuang \n shen
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
#普通的值 [数字,布尔值,字符串]
name : "mou \n ku"
#对象,Map格式
student :
name : mhqdz
age : 17
#对象的行内写法,Typora这个name没亮是bug?idea里明明亮了的
teacher : {name: mhqdz,age : 18 }
#数组
pets :
- cat
- dog
- pig
#行内写法
arr : [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]
1
2
3
#更改端口号,等价properties里的server.port=8081
server :
port : 8082
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
package com.mhqdz.pojo ;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties ;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component ;
//将该类标记为Spring中的一个Bean
@Component
//此类中的属性将与application文件中的"person"类中的同名属性属性绑定
@ConfigurationProperties ( "person" )
public class Dog {
private String name ;
private Integer age ;
private Cat cat ;
public Dog () {
}
public Cat getCat () {
return cat ;
}
public void setCat ( Cat cat ) {
this . cat = cat ;
}
public Dog ( String name , Integer age , Cat cat ) {
this . name = name ;
this . age = age ;
this . cat = cat ;
}
public String getName () {
return name ;
}
public void setName ( String name ) {
this . name = name ;
}
public Integer getAge () {
return age ;
}
public void setAge ( Integer age ) {
this . age = age ;
}
@Override
public String toString () {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", cat=" + cat . toString () +
'}' ;
}
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
#application.yaml
person :
name : mhqdz
age : 17
cat :
name : bbd
age : 3
==松散绑定==
比如yml中写的last-name,和lastName是一样的,-后面跟着的字母默认是大写的 这就是松散绑定
在字段是增加一层过滤器验证以保证数据的合法性(比如对于年龄字段,如果值小于0或者非常大就是不合法的)
因为比较简单所以直接上例子:@Validated //开启数据校验别忘了就好其他设置就去读源码就行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
package com.mhqdz.pojo ;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties ;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component ;
import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated ;
import javax.validation.constraints.Email ;
import javax.validation.constraints.Max ;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min ;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull ;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties ( "person" )
@Validated //开启数据校验
public class Dog {
// @Email注解报红 是因为新版本需要validation启动器
// <dependency>
// <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
// <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validation</artifactId>
// </dependency>
@Email ( message = "邮箱格式错误" ) //message设置报错时的信息
@NotNull ( message = "名字不能为空" )
private String name ;
@Max ( value = 120 , message = "年龄最大不能超过过120" )
@Min ( value = 0 , message = "年龄不能小于0" )
private Integer age ;
private Cat cat ;
public Dog () {
}
public Cat getCat () {
return cat ;
}
public void setCat ( Cat cat ) {
this . cat = cat ;
}
public Dog ( String name , Integer age , Cat cat ) {
this . name = name ;
this . age = age ;
this . cat = cat ;
}
public String getName () {
return name ;
}
public void setName ( String name ) {
this . name = name ;
}
public Integer getAge () {
return age ;
}
public void setAge ( Integer age ) {
this . age = age ;
}
@Override
public String toString () {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", cat=" + cat . toString () +
'}' ;
}
}
使用的数据还是上面的,成功报错:Field error in object ‘person’ on field ’name’: rejected value [mhqdz]; codes [Email.person.name,Email.name,Email.java.lang.String,Email]; arguments [org.springframework.context.support.DefaultMessageSourceResolvable: codes [person.name,name]; arguments []; default message [name],[Ljavax.validation.constraints.Pattern$Flag;@4cfa8227,.*]; default message [邮箱格式错误]; origin class path resource [application.yaml] - 2:9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
@NotNull ( message = "名字不能为空" )
private String userName ;
@Max ( value = 120 , message = "年龄最大不能查过120" )
private int age ; @Email ( message = "邮箱格式错误" ) private String email ;
空检查
@Null 验证对象是否为 null
@NotNull 验证对象是否不为 null , 无法查检长度为 0 的字符串
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是 Null 还有被 Trim 的长度是否大于 0 , 只对字符串 , 且会去掉前后空格 . @NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为 NULL 或者是 EMPTY . Booelan 检查
@AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
@AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
长度检查
@Size ( min =, max =) 验证对象( Array , Collection , Map , String )长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Length ( min =, max =) string is between min and max included .
日期检查
@Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
@Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
@Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
实际环境中,文件名可以是 application-{profile}.properties/yml,用来指定多个环境版本
如:
application-test.yaml 代表测试环境配置
application-dev.yaml 代表开发环境配置
但是Springboot并不会直接启动这些配置文件,它默认使用application.yaml主配置文件
profile是Spring对不同环境提供不同配置功能的支持,可以通过激活不同的环境版本,实现快速切换环境
在application.yaml中配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
#spring.profiles.active的方法已弃用,现在官方更推荐下面的spring.config.activate.on-profile的方法
#这是为了提升对 Kubernetes 的原生支持而作的修改
spring :
profiles :
active : dev
---
spring :
config :
activate :
on-profile : dev
即可把环境切换到application-dev.yaml
例:
1
2
3
#application-dev.yaml
server :
port : 8081
1
2
3
#application-test.yaml
server :
port : 8082
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
#application.yaml
server :
port : 8080
#如果到处为止的话就会默认开8080端口
#加上下面这一行的话就会使用application-dev.yaml文件作为环境而打开8081端口,test同理
spring :
profiles :
active : dev
==yaml的多文档块==
==.yaml==文件可以用---把多个文件里的东西以文档块的方式分割,从而把多个环境放到一个文件下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
server :
port : 8080
spring :
profiles :
active : dev #调用
---
server :
port : 8081
spring :
config :
activate :
on-profile : dev #配置名称
---
server :
port : 8082
spring :
config :
activate :
on-profile : test
多文档块的方式适用于配置较少的情况,为了后续看着方便,如果配置比较多还是推荐分文件的方式
静态资源处理
SpringBoot中,SpringMVC的web配置都在 WebMvcAutoConfiguration 这个配置类里面;
我们可以去看看 WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter 中有很多配置方法;
有一个方法:addResourceHandlers 添加资源处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
public void addResourceHandlers ( ResourceHandlerRegistry registry ) {
if (! this . resourceProperties . isAddMappings ()) {
logger . debug ( "Default resource handling disabled" );
} else {
this . addResourceHandler ( registry , "/webjars/**" , "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/" );
this . addResourceHandler ( registry , this . mvcProperties . getStaticPathPattern (), ( registration ) -> {
registration . addResourceLocations ( this . resourceProperties . getStaticLocations ());
if ( this . servletContext != null ) {
ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource ( this . servletContext , "/" );
registration . addResourceLocations ( new Resource []{ resource });
}
});
}
}
所有的 /webjars/** ,都需要去classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/找对应的资源
在Resources.class;中
1
private static final String [] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String []{ "classpath:/META-INF/resources/" , "classpath:/resources/" , "classpath:/static/" , "classpath:/public/" };
它会先去,CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS数组里面的路径去找资源,然后再去webjars映射路径目录下找资源,最后会直接在当前目录下找资源
在上述文件夹下的资源都可以直接拿到
一般而言
public:放一些公共资源比如大家都能访问的一些js文件
static:放一些静态资源比如各种图片
resources:放上传的文件
优先级:resource>static>public,不是因为resource重要一点public垃圾一点,而是因为它在遍历CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS数组的时候是按照这个顺序的而已
特别的templates文件夹只能通过controller读到
==主页==:它会在上述的三个文件夹中找名为index.html的文件作为主页
==webjars==
Webjars本质就是以jar包的方式引入我们的静态资源,我们以前要导入一个静态资源文件,直接导入即可
即可以把静态资源用maven导入
仓库:WebJars - Web Libraries in Jars
Thymeleaf是Springboot官方支持的模板引擎,有着动静分离等独有特点
==模板引擎==
模板引擎,我们其实大家听到很多,其实jsp就是一个模板引擎,还有用的比较多的freemarker,包括SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf,模板引擎有非常多,但再多的模板引擎,他们的思想都是一样的:前端文件中留一些标识,后端为那些标识赋予意义,模板引擎连接这些数据
==引入Thymeleaf==
Thymeleaf 官网
在Github 的主页
Spring官方文档
==Thymeleaf引用路径==
ThymeleafProperties文件中有如下配置,
1
2
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/" ;
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html" ;
所以它会去扫描templates/templates文件夹下的所有html文件
==例1==
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
//controller文件
@RequestMapping ( "/t1" )
public String test1 ( Model model ){
//存入数据
model . addAttribute ( "msg" , "Hello,Thymeleaf" );
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test" ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
//templates/test.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
< html lang = "en" xmlns:th = "http://www.thymeleaf.org" > //命名空间的约束
< head >
< meta charset = "UTF-8" >
< title > 大标题</ title >
</ head >
< body >
< h1 > 测试页面</ h1 >
<!--th:text就是将div中的内容设置为它指定的值,和之前学习的Vue一样-->
< div th:text = "${msg}" ></ div >
</ body >
</ html >
要使用thymeleaf,需要在html文件中导入命名空间的约束:xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
==Thymeleaf 语法==
Thymeleaf中文教程
简单表达式:
Variable expressions(变量表达式)${...}
Selection expressions(选择表达式)*{...}
Message (i18n) expressions(消息表达式) #{...}
Link (URL) expressions(链接表达式)@{...}
Fragment expressions(分段表达式)~{...}
==例2==
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
//controller文件
@RequestMapping ( "/t2" )
public String test2 ( Map < String , Object > map ){
//存入数据
map . put ( "msg" , "<h1>Hello</h1>" );
map . put ( "users" , Arrays . asList ( "qinjiang" , "kuangshen" ));
//classpath:/templates/test.html
return "test" ;
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
//templates/test.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
< html lang = "en" xmlns:th = "http://www.thymeleaf.org" >
< head >
< meta charset = "UTF-8" >
< title > 狂神说</ title >
</ head >
< body >
< h1 > 测试页面</ h1 >
< div th:text = "${msg}" ></ div >
<!--不转义-->
< div th:utext = "${msg}" ></ div >
<!--遍历数据-->
<!--th:each每次遍历都会生成当前这个标签:官网#9-->
< h4 th:each = "user :${users}" th:text = "${user}" ></ h4 >
< h4 >
<!--行内写法:官网#12-->
< span th:each = "user:${users}" > [[${user}]]</ span >
</ h4 >
</ body >
</ html >
在进行项目编写前,我们还需要知道一个东西,就是SpringBoot对我们的SpringMVC还做了哪些配置,包括如何扩展,如何定制。
只有把这些都搞清楚了,我们在之后使用才会更加得心应手,途径一:源码分析 ,途径二:官方文档
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
Spring MVC Auto - configuration
// Spring Boot为Spring MVC提供了自动配置,它可以很好地与大多数应用程序一起工作。
Spring Boot provides auto - configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications .
// 自动配置在Spring默认设置的基础上添加了以下功能:
The auto - configuration adds the following features on top of Spring ’ s defaults :
// 包含视图解析器
Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans .
// 支持静态资源文件夹的路径,以及webjars
Support for serving static resources , including support for WebJars
// 自动注册了Converter:
// 转换器,这就是我们网页提交数据到后台自动封装成为对象的东西,比如把"1"字符串自动转换为int类型
// Formatter:【格式化器,比如页面给我们了一个2019-8-10,它会给我们自动格式化为Date对象】
Automatic registration of Converter , GenericConverter , and Formatter beans .
// HttpMessageConverters
// SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的的,比如我们要把一个User对象转换为JSON字符串,可以去看官网文档解释;
Support for HttpMessageConverters ( covered later in this document ).
// 定义错误代码生成规则的
Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver ( covered later in this document ).
// 首页定制
Static index . html support .
// 图标定制
Custom Favicon support ( covered later in this document ).
// 初始化数据绑定器:帮我们把请求数据绑定到JavaBean中!
Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean ( covered later in this document ).
/*
如果您希望保留Spring Boot MVC功能,并且希望添加其他MVC配置(拦截器、格式化程序、视图控制器和其他功能),则可以添加自己
的@configuration类,类型为webmvcconfiguer,但不添加@EnableWebMvc。如果希望提供
RequestMappingHandlerMapping、RequestMappingHandlerAdapter或ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver的自定义
实例,则可以声明WebMVCregistrationAdapter实例来提供此类组件。
*/
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features and you want to add additional MVC configuration
( interceptors , formatters , view controllers , and other features ), you can add your own
@Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide
custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping , RequestMappingHandlerAdapter , or
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver , you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance to provide such components .
// 如果您想完全控制Spring MVC,可以添加自己的@Configuration,并用@EnableWebMvc进行注释。
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC , you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
新建项目
引入Spring Web、JDBC API和MySQL Driver,其他随意
编写application.yaml
1
2
3
4
5
6
spring :
datasource :
username : root
password : 123456
url : jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_library?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=true
driver-class-name : com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
去test里面测试一下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
package com.mhqdz ;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test ;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired ;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest ;
import javax.sql.DataSource ;
import java.sql.Connection ;
import java.sql.SQLException ;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringBootSqlApplicationTests {
@Autowired
DataSource dataSource ;
@Test
void contextLoads () throws SQLException {
System . out . println ( dataSource . getClass ());
Connection connection = dataSource . getConnection ();
System . out . println ( connection );
connection . close ();
}
}
直接JDBCController
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
package com.mhqdz.controller ;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired ;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate ;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping ;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping ;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController ;
import java.util.List ;
import java.util.Map ;
@RestController
@RequestMapping ( "/jdbc" )
public class JDBCController {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate ;
@GetMapping ( "/query" )
public List < Map < String , Object >> userList (){
String sql = "select * from db_library.user" ;
return jdbcTemplate . queryForList ( sql );
}
}
导入druid和Log4j 的依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId> com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId> druid</artifactId>
<version> 1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId> log4j</groupId>
<artifactId> log4j</artifactId>
<version> 1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
配置yaml
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
spring :
datasource :
username : root
password : 123456
url : jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_library?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=true
driver-class-name : com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
type : com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Spring Boot 默认是不注入这些属性值的,需要自己绑定
#druid 数据源专有配置
initialSize : 5
minIdle : 5
maxActive : 20
maxWait : 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis : 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis : 300000
validationQuery : SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle : true
testOnBorrow : false
testOnReturn : false
poolPreparedStatements : true
#配置监控统计拦截的filters,stat:监控统计、log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sql注入
#如果允许时报错 java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority
#则导入 log4j 依赖即可,Maven 地址:https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j
filters : stat,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize : 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat : true
connectionProperties : druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
配完type就连上了剩下的是它的配置
com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource基本配置参数如下
在config.DruidConfig里自己绑定DruidDataSource的全局配置文件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
package com.mhqdz.config ;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource ;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet ;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties ;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean ;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean ;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration ;
import javax.sql.DataSource ;
import java.util.HashMap ;
import java.util.Map ;
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
/*
将自定义的 Druid数据源添加到容器中,不再让 Spring Boot 自动创建
绑定全局配置文件中的 druid 数据源属性到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource从而让它们生效
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource"):作用就是将 全局配置文件中
前缀为 spring.datasource的属性值注入到 com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 的同名参数中
*/
@ConfigurationProperties ( prefix = "spring.datasource" )
@Bean
public DataSource druidDataSource (){
return new DruidDataSource ();
}
}
配置数据源监控以及过滤器filter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
package com.mhqdz.config ;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource ;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet ;
import com.alibaba.druid.support.http.WebStatFilter ;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties ;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean ;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.ServletRegistrationBean ;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean ;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration ;
import javax.sql.DataSource ;
import java.util.Arrays ;
import java.util.HashMap ;
import java.util.Map ;
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig {
@ConfigurationProperties ( prefix = "spring.datasource" )
@Bean
public DataSource druidDataSource (){
return new DruidDataSource ();
}
//配置 Druid 监控管理后台的Servlet;
//内置 Servlet 容器时没有web.xml文件,所以使用 Spring Boot 的注册 Servlet 方式
//配置完这个就可以在web上看到监控信息了
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet () {
ServletRegistrationBean bean = new ServletRegistrationBean ( new StatViewServlet (), "/druid/*" );
// 这些参数可以在 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet
// 的父类 com.alibaba.druid.support.http.ResourceServlet 中找到
Map < String , String > initParams = new HashMap <>();
initParams . put ( "loginUsername" , "admin" ); //后台管理界面的登录账号
initParams . put ( "loginPassword" , "123456" ); //后台管理界面的登录密码
//后台允许谁可以访问
//initParams.put("allow", "localhost"):表示只有本机可以访问
//initParams.put("allow", ""):为空或者为null时,表示允许所有访问
initParams . put ( "allow" , "" );
//deny:Druid 后台拒绝谁访问
//initParams.put("kuangshen", "192.168.1.20");表示禁止此ip访问
//设置初始化参数
bean . setInitParameters ( initParams );
return bean ;
}
//配置 Druid 监控 之 web 监控的 filter
//WebStatFilter:用于配置Web和Druid数据源之间的管理关联监控统计
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter () {
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean ();
bean . setFilter ( new WebStatFilter ());
//exclusions:设置哪些请求进行过滤排除掉,从而不进行统计
Map < String , String > initParams = new HashMap <>();
initParams . put ( "exclusions" , "*.js,*.css,/druid/*,/jdbc/*" );
bean . setInitParameters ( initParams );
//"/*" 表示过滤所有请求
bean . setUrlPatterns ( Arrays . asList ( "/*" ));
return bean ;
}
}
新建项目
引入Spring Web、JDBC API和MySQL Driver,其他随意
导入MyBatis依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
<!--它是mybatis-spring开头,而非spring-boot-starter由此可知它不是官方的:整合mybatis和springBoot-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.spring.boot/mybatis-spring-boot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId> org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId> mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version> 2.1.4</version>
配置数据库连接信息
1
2
3
4
5
6
spring :
datasource :
username : root
password : 123456
url : jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_library?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=true
driver-class-name : com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
测试数据库连接,同JDBC
pojo里创建实体类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
package com.mhqdz.pojo ;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor ;
import lombok.Data ;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor ;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class DbLibrary {
String name ;
int lv ;
int id ;
}
创建mapper接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
package com.mhqdz.mapper ;
import com.mhqdz.pojo.DbLibrary ;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository ;
import java.util.List ;
//@Mapper//表示这是mybatis的mapper类,因为已经在Application文件里配置了@MapperScan("com.mhqdz.mapper")会扫描包,所以这里可以省略
@Repository //将类识别为Bean,且将所标注的类中抛出的数据访问异常封装为 Spring 的数据访问异常类型
public interface DbLibraryMapper {
List < DbLibrary > queryAll ();
}
在Application文件里配置了@MapperScan(“com.mhqdz.mapper”)直接扫描包,可以在mapper接口里一个一个配置@Mapper
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
package com.mhqdz ;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan ;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication ;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication ;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan ( "com.mhqdz.mapper" )
public class SpringBootMybatisApplication {
public static void main ( String [] args ) {
SpringApplication . run ( SpringBootMybatisApplication . class , args );
}
}
mapper接口的实现文件(resources/mybatis/mapper/mapper.xml)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace= "com.mhqdz.mapper.DbLibraryMapper" >
<select id= "queryAll" resultType= "DbLibrary" >
SELECT * from db_library.user
</select>
</mapper>
在Application文件中把资源类和mapper整合进去,其他配置看源码吧
1
2
3
4
#整合mybatis
mybatis :
type-aliases-package : com.mhqdz.pojo
mapper-locations : classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
因为功能少所以不整service了,直接新建controller测试
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
package com.mhqdz.controller ;
import com.mhqdz.mapper.DbLibraryMapper ;
import com.mhqdz.pojo.DbLibrary ;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired ;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping ;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController ;
import java.util.List ;
@RestController
public class DbLibraryController {
@Autowired
private DbLibraryMapper dbLibraryMapper ;
@GetMapping ( "queryAll" )
public List < DbLibrary > queryAll (){
List < DbLibrary > list = dbLibraryMapper . queryAll ();
for ( DbLibrary i : list ){
System . out . println ( i . toString ());
}
return list ;
}
}